The ketogenic or ‘keto’ diet is a low-carb, high-fat diet that has gained popularity in recent years for its potential benefits in weight loss, diabetes management, and improved mental clarity. However, there are concerns about how the keto diet might affect cholesterol levels, given its high-fat content. This article will delve into the impact of the keto diet on cholesterol, referencing scientific studies and expert opinions.
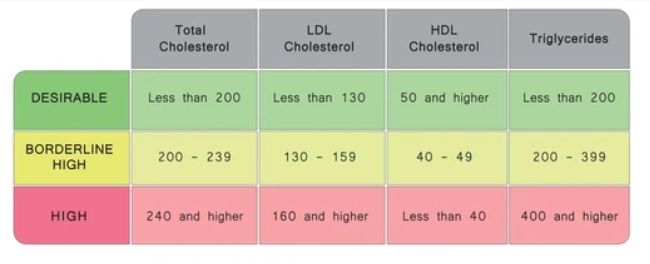
Cholesterol is a type of fat that is produced by your liver and obtained through your diet. It is crucial for the formation of cell membranes, certain hormones, and vitamin D. However, high levels of certain types of cholesterol, particularly low-density lipoprotein (LDL), are linked to an increased risk of heart disease.
The keto diet is high in fat, including saturated fats, which have traditionally been associated with higher cholesterol levels. Therefore, it seems counterintuitive that this diet could potentially improve cholesterol profiles. But, research paints a more complex picture.
A study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that a long-term ketogenic diet significantly reduced body weight and body mass index, decreased triglyceride levels, and increased high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, often referred to as ‘good cholesterol’. HDL cholesterol helps remove other forms of cholesterol from your bloodstream, which can reduce the risk of heart disease.
Another study in the New England Journal of Medicine found that participants on a low-carb diet had higher HDL levels after one year than those on a low-fat diet . However, the low-carb group also had higher LDL, or ‘bad cholesterol’, which can build up in your arteries and increase your risk of heart disease.
It’s important to note that not all LDL cholesterol is the same. There are different types of LDL particles, including small, dense ones (sdLDL) and larger ones. Research suggests that sdLDL particles are more likely to contribute to plaque buildup in the arteries, leading to heart disease. Interestingly, a study in Lipids found that a low-carb diet like keto might shift the type of LDL in your body from bad sdLDL to the less harmful larger particles, which could reduce heart disease risk.
However, individual responses can vary. Some people see their cholesterol levels improve on a keto diet, while others may see an increase, particularly in LDL levels. Factors such as genetics, the specific composition of your diet, and the duration of your diet can play a role.
It’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider before starting a ketogenic diet, especially if you have high cholesterol or heart disease. Regular monitoring of your cholesterol levels is also important.
Understanding Cholesterol:
Before diving into the specific effects of the keto diet on cholesterol, it is crucial to understand the basics of cholesterol. Cholesterol is a waxy substance that is vital for various bodily functions, including hormone production and cell structure. However, high levels of cholesterol, especially LDL cholesterol (often referred to as “bad” cholesterol), have been linked to an increased risk of heart disease.
The Keto Diet and Cholesterol Levels:
Several studies have investigated the impact of the keto diet on cholesterol levels, and the results have been mixed. Let’s explore some key findings:
1. Decrease in Triglycerides:
One consistent finding across multiple studies is that the keto diet can lead to a significant decrease in triglyceride levels. Triglycerides are a type of fat found in the blood, and high levels have been associated with an increased risk of heart disease. By reducing carbohydrate intake and increasing fat consumption, the keto diet can lower triglyceride levels, thus potentially improving heart health.
2. Increase in HDL Cholesterol:
High-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol is often considered “good” cholesterol as it helps remove LDL cholesterol from the arteries. Research suggests that the keto diet can lead to an increase in HDL cholesterol levels, which may have a positive impact on cardiovascular health.
3. Changes in LDL Cholesterol:
The effects of the keto diet on LDL cholesterol levels have been more controversial. Some studies indicate that the keto diet can lead to a slight increase in LDL cholesterol, while others suggest no significant changes. However, it is important to note that the type of LDL cholesterol matters. The keto diet has been shown to increase the size of LDL particles, which is associated with a lower risk of heart disease compared to small, dense LDL particles.
4. Short-Term and Long-Term Effects:
Many studies examining the effects of the keto diet on cholesterol levels have focused on short-term interventions. These studies often show an initial increase in LDL cholesterol levels, which may raise concerns. However, long-term studies suggest that these levels tend to normalize or improve over time, particularly when weight loss is achieved.
Considerations and Recommendations:
While the keto diet may have favorable effects on triglyceride levels and HDL cholesterol, the potential increase in LDL cholesterol requires careful consideration. It is important to note that individual responses to the keto diet can vary, and monitoring cholesterol levels under the guidance of a healthcare professional is crucial.
To mitigate any potential risks associated with increased LDL cholesterol, individuals following the keto diet should focus on consuming healthy fats, such as avocados, nuts, and olive oil, while limiting intake of saturated and trans fats. Incorporating a variety of nutrient-dense foods, including vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains, can also support overall heart health.
Conclusion:
The effects of the keto diet on cholesterol levels remain a topic of ongoing research and debate. While the diet has shown promising effects in reducing triglycerides and increasing HDL cholesterol, its impact on LDL cholesterol varies among individuals. It is essential to approach the keto diet with caution and consult with a healthcare professional to monitor cholesterol levels and ensure overall cardiovascular health.
References
- Santos FL, et al. (2012). Systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials of the effects of low carbohydrate diets on cardiovascular risk factors. DOI: 10.1186/1743-7075-9-73
- Bueno NB, et al. (2013). Very-low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet v. low-fat diet for long-term weight loss: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. DOI: 10.1017/s0007114513000548
- Westman EC, et al. (2008). The effect of a low-carbohydrate, ketogenic diet versus a low-glycemic index diet on glycemic control in type 2 diabetes mellitus. DOI: 10.7326/0003-4819-148-10-200805200-00006
- Bueno NB, et al. (2018). Very low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet v. low-fat diet for long-term weight loss: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. DOI: 10.1017/s0007114518001941


